Date:2025-08-06 Views:1019
Japan begann bereits im 20. Jahrhundert mit der Produktion von Pulvermetallurgie-Teilen.
Die Abbildungen 5-2 bis 5-6 zeigen verschiedene Pulvermetallurgie-Teile, die in unterschiedlichen Komponenten japanischer Motorräder verwendet werden. Tabelle 5-3 listet die technischen Bedingungen einiger dieser Teile auf. Abbildung 5-7 ist ein schematisches Diagramm der in Tabelle 5-3 aufgeführten Pulvermetallurgie-Teile.
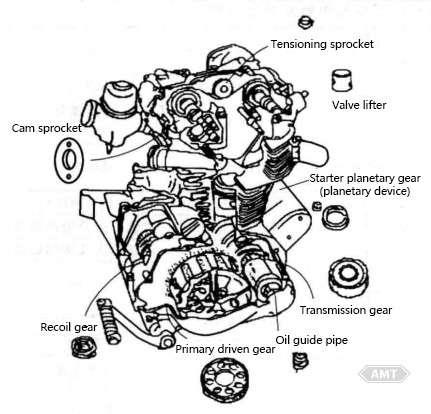
Abbildung 5-2 Pulvermetallurgie-Teile in japanischen Viertakt-Motorradmotoren
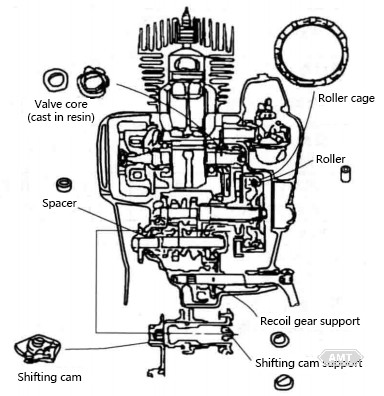
Abbildung 5-3 Pulvermetallurgie-Teile in japanischen Zweitakt-Motorradmotoren
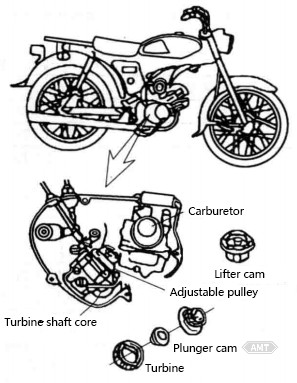
Abbildung 5-4 Pulvermetallurgie-Teile in Pumpen für japanische selbstschmierende Zweitakt-Motorräder
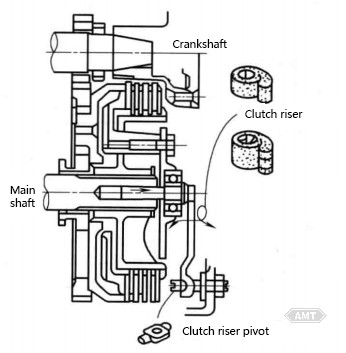
Abbildung 5-5 Pulvermetallurgie-Teile in japanischen Motorradkupplungen
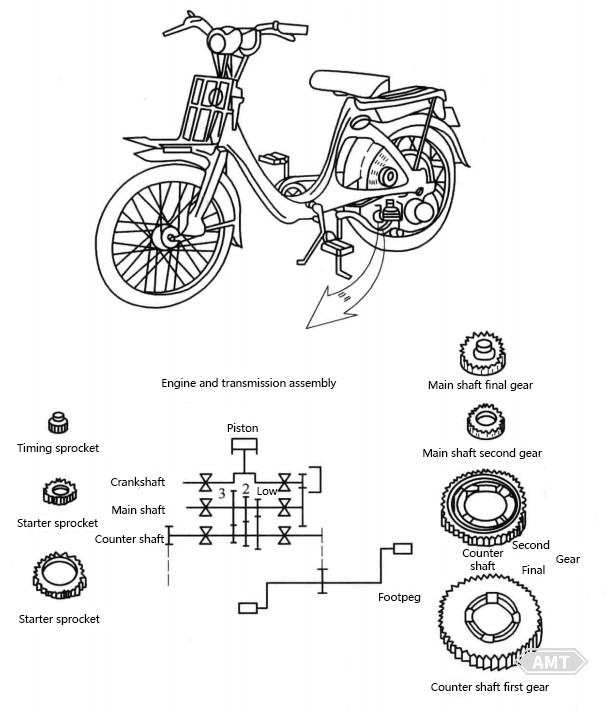
Abbildung 5-6 Pulvermetallurgie-Teile im Getriebe kleiner japanischer Motorräder
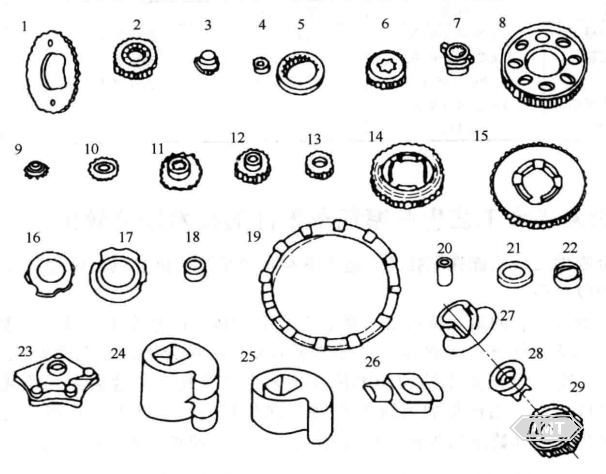
Abbildung 5-7 Schematische Darstellung der in Tabelle 5-3 aufgeführten Pulvermetallurgie-Teile
Tabelle 5-3 listet die technischen Bedingungen von Pulvermetallurgie-Teilen für Motorräder auf
Teilname | Material | Dichte (g/cm3) | Nachbehandlung | Nitto-Materialgrad | Anmerkungen |
Viertakt-Motor | |||||
1. Nockenrad | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,7~1,0)C | 6,9~7,2 | - | 18EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
2. Rückschlagrad | Fe-(1~3)Ni-(0,3~0,6)Mo-(0,05~0,25)Mn-(0,15~0,3)C | 7,6~7,8 | Aufkohlen und Härten | HN-15 | Schmiedefestigkeit, Verschleißfestigkeit |
3. Spannvorrichtungsrad | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,7~1,0)C | 6,6~6,8 | - | 18EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
4. Starter-Reduktionsgetriebe (innen) | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,9~7,2 | Aufkohlen und Härten | 14EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
5. Starter-Reduktionsgetriebe (außen) | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,6~6,9 | - | 14EPC | - |
6. Primäres Antriebsrad | Fe-(1~3)Ni-(0,3~0,6)Mo-(0,05~0,25)Mn-(0,15~0,3)C | 7,6~7,8 | Aufkohlen und Härten | HN-15 | Schmiedefestigkeit, Verschleißfestigkeit |
7. Öl-Leitrohr | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,6~6,9 | Aufkohlen und Härten | 14EPC | Gleiteigenschaften |
8. Primäres Abtriebsrad | Fe-(1~3)Cu-(2~4)Ni-(0,3~0,6)C | 6,9~7,2 | Hochfrequenz-Härten | ENK | Verschleißfestigkeit |
50cc-Motorradmotor |
|
|
|
|
|
9. Steuerrad | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,7~1,0)C | 6,6~6,9 | - | 18EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
10. Starter-Ritzel (1) | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,7~1,0)C | 6,6~6,9 | - | 18EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
11. Starter-Ritzel (2) | Fe-(2~4)Ni-(0,5~1,0)Mn-(0,2~0,4)C | 6,9~7,2 | Aufkohlen und Härten | EN | Verschleißfestigkeit |
12. Hauptwelle-Hinterrad | Fe-(2~4)Ni-(0,5~1,0)Mn-(0,2~0,4)C | 6,9~7,2 | Aufkohlen und Härten | EN | Verschleißfestigkeit |
13. Hauptwelle-Zweitrad | Fe-(2~4)Ni-(0,5~1,0)Mn-(0,2~0,4)C | 6,9~7,2 | Aufkohlen und Härten | EN | Verschleißfestigkeit |
14. Gegenzweitrad-Vorderrad | Fe-(2~4)Ni-(0,5~1,0)Mn-(0,2~0,4)C | 6,9~7,2 | Aufkohlen und Härten | EN | Verschleißfestigkeit |
15. Gegenerstes Rad | Fe-(2~4)Ni-(0,5~1,0)Mn-(0,2~0,4)C | 6,9~7,2 | Aufkohlen und Härten | EN | Verschleißfestigkeit |
Zweitakt-Motor |
|
|
|
|
|
16. Ventilkern | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,3~6,6 | Wärmebehandlung | 14EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
17. Distanzstück | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,7~1,0)C | 6,6~6,9 | - | 18EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
18. Rollenhalter | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,3~6,6 | Dampfbehandlung | 14EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
19. Rolle | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,7~1,0)C | 6,6~6,9 | Dampfbehandlung | 18EPC | - |
20. Rückschlagwelle | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,6~6,9 | - | 14EPC | - |
21. Schaltnockenwelle | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,6~6,9 | - | 14EPC | - |
22. Schaltnocken | Fe-(2~4)Ni-(0,5~1,0)Mn-(0,2~0,4)C | 6,6~7,1 | Aufkohlen und Härten | EN | Verschleißfestigkeit |
Kupplung |
|
|
|
|
|
23. Kupplungs-Hebenocken | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,9~7,2 | Aufkohlen und Härten | 14EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
24. Kupplungs-Heberolle | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,9~7,2 | Hochfrequenz-Härten | 14EPC | - |
25. Kupplungs-Hebewelle | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,6~6,9 | Aufkohlen und Härten | 14EPC | - |
Pumpe |
|
|
|
|
|
26. Verstellbare Riemenscheibe | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,3~6,6 | Dampfbehandlung | 14EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
27. Plunger-Nocken | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,3~6,6 | Vollständige chemische Plattierung, Ni-P | 14EPC | Verschleißfestigkeit |
28. Turbine | Fe-(1~2)Cu-(0,4~0,7)C | 6,3~6,6 | Dampfbehandlung | 14EPC | - |
Abbildung 5-8 zeigt einige Pulvermetallurgie-Teile für Motorräder. Tabelle 5-4 listet die technischen Bedingungen der in Abbildung 5-8 gezeigten Pulvermetallurgie-Teile auf.
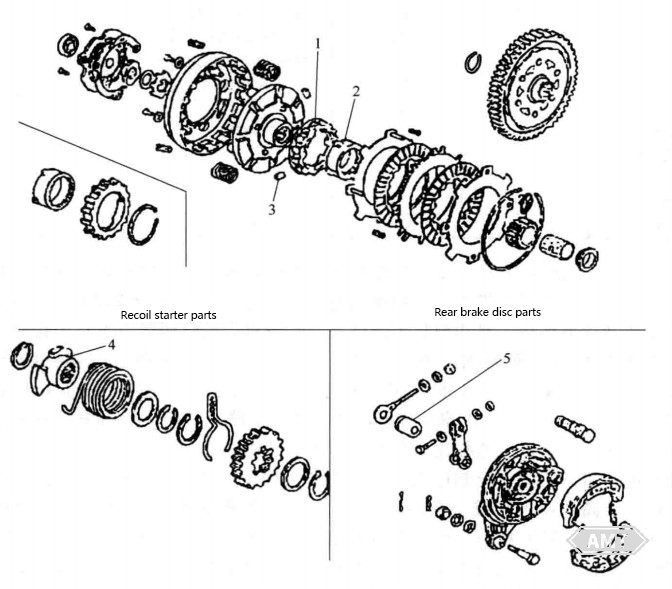
Abbildung 5-8 Einige Pulvermetallurgie-Teile für Motorräder
Tabelle 5-4 Technische Bedingungen der in Abbildung 5-8 gezeigten Pulvermetallurgie-Teile für Motorräder
Teilname | Material | Dichte (g/cm3) | Nachbehandlung | Erforderliche Eigenschaften |
1. Kupplungsnabe | Fe-2,0Cu-0,7C | 6,7~7,0 | Aufkohlen und Härten | Verschleißfestigkeit |
2. Äußeres Getrieberad | Fe-2,0Cu-0,7C | 6,7~7,0 | Aufkohlen und Härten | Verschleißfestigkeit |
3. Rolle | Fe-2,0Cu | 7,0~7,4 | Aufkohlen und Härten | Verschleißfestigkeit |
4. Reaktionsfederbuchse | Fe-2,0Cu-0,7C | 6,7~7,0 | - | Schlagfestigkeit |
5. Scheibenbuchse | CD-2 | 6,5~7,0 | - | Druckfestigkeit, Verschleißfestigkeit |
Leave your email for more ebooks and prices📫 !
Kontakt:Fidel
Tel:021-5512-8901
Mobil:19916725892
E-Mail:sales1@atmsh.com
Adresse:Nr. 398 Guiyang-Straße, Yangpu, China